Our Concrete Mix Quantity Calculator simplifies construction planning by providing accurate estimates of cement, sand, aggregate, and water based on mix design. Whether you’re working on slabs, beams, or columns, this tool saves time, ensures quality, and optimizes costs.
Cement Concrete Calculator
Select the mix ratio, enter the volume or dimensions, and instantly get the material quantities.
Results
| Sr. | Material | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cement | |
| 2 | Sand | |
| 3 | Aggregate |
Material Share (Pie Chart)
Strong concrete starts with the right mix. If the cement–sand–aggregate ratio is off, you can end up with weak strength, excess shrinkage cracks, or unnecessary material cost. This calculator helps you estimate material quantities for common M-grade nominal mixes (M5 to M25) using either total volume or length × width × depth.
What you’ll get instantly: cement (bags + kg + volume), sand volume, aggregate volume, and wet/dry volume.
How to Use the Concrete Calculator
- Select the concrete grade (example: M20 = 1 : 1.5 : 3).
- Choose input method: Volume (m³/ft³) or Dimensions (L × W × Depth in m/ft).
- Optional: Adjust Dry Volume Factor (default 1.54) and cement bag size (50 kg / 40 kg).
- Click Calculate to view material quantities and the mix-share chart.

Concrete Mix Ratios (M-Grade) Explained
In nominal mixes, the ratio is written as Cement : Sand : Aggregate. Example: M20 = 1 : 1.5 : 3 means 1 part cement, 1.5 parts sand, and 3 parts aggregate.
| Concrete Grade | Nominal Mix Ratio | Common Use (General Guidance) |
|---|---|---|
| M5 | 1 : 5 : 10 | Blinding / non-structural |
| M7.5 | 1 : 4 : 8 | Light-duty non-structural |
| M10 | 1 : 3 : 6 | Light structural works |
| M15 | 1 : 2 : 4 | General construction |
| M20 | 1 : 1.5 : 3 | Residential & commercial (common) |
| M25 | 1 : 1 : 2 | Higher strength applications |

What the Calculator Calculates (Inputs & Outputs)
Inputs
- Concrete grade (M5–M25).
- Volume in m³ or ft³ OR Dimensions (L × W × Depth) in meters/feet.
- Dry Volume Factor (default 1.54) — adjustable for practical site conditions.
- Cement bag size (50 kg or 40 kg).
Outputs
- Cement: bags + kg + volume (m³/ft³)
- Sand: volume (m³/ft³)
- Aggregate: volume (m³/ft³)
- Wet & dry volume (m³/ft³) + the factor used
Note: If you also want to estimate mixing water, see the “Water Estimate” section below (optional guidance).
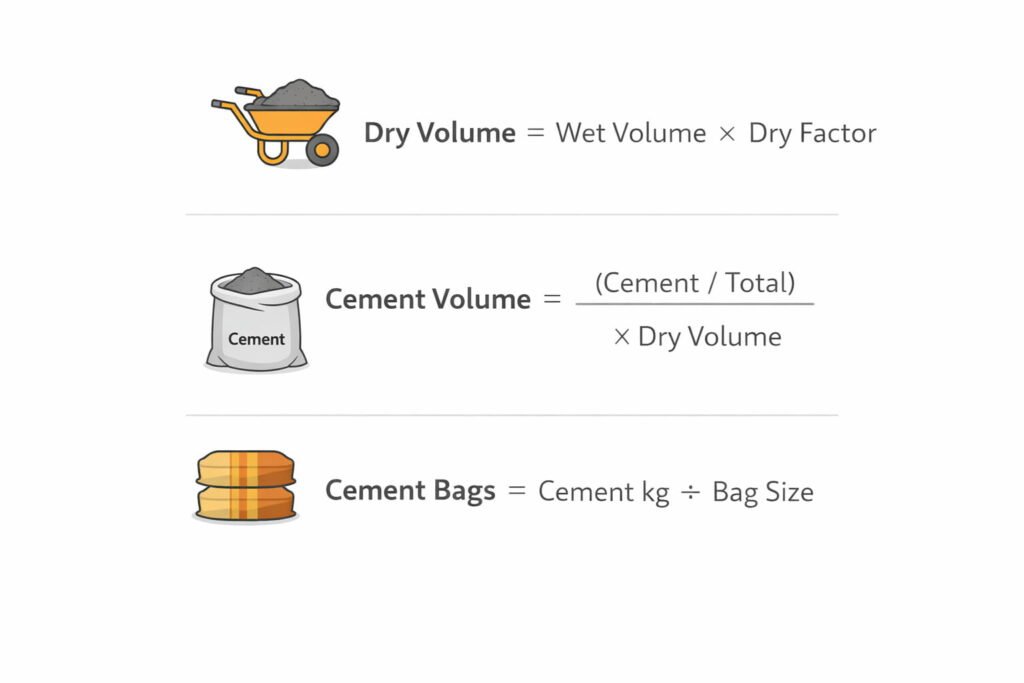
Formulas Used (Shown Clearly)
The calculator uses standard nominal mix logic with a dry volume adjustment. These formulas are shown in a readable format:
- Dry Volume = Wet Volume × Dry Factor
- Total Ratio = Cement + Sand + Aggregate
- Cement Volume = (Cement / Total Ratio) × Dry Volume
- Sand Volume = (Sand / Total Ratio) × Dry Volume
- Aggregate Volume = (Aggregate / Total Ratio) × Dry Volume
- Cement Weight (kg) = Cement Volume × 1440 (kg/m³ density)
- Cement Bags = Cement Weight ÷ Bag Size
Worked Example: 1 m³ of M20 Concrete (1 : 1.5 : 3)
This example helps you understand the logic behind the tool. Assume:
- Wet Volume = 1.00 m³
- Dry Factor = 1.54
- Cement density = 1440 kg/m³
- Bag size = 50 kg
Step 1: Convert wet volume to dry volume
Dry Volume = 1.00 × 1.54 = 1.54 m³
Step 2: Total ratio
Total = 1 + 1.5 + 3 = 5.5
Step 3: Material volumes
- Cement Volume = (1 / 5.5) × 1.54 = 0.28 m³
- Sand Volume = (1.5 / 5.5) × 1.54 = 0.42 m³
- Aggregate Volume = (3 / 5.5) × 1.54 = 0.84 m³
Step 4: Cement weight and bags
- Cement Weight = 0.28 × 1440 = 403.2 kg
- Cement Bags (50 kg) = 403.2 ÷ 50 = 8.06 bags
Quick summary for 1 m³ (M20):
- Cement: 8.06 bags (403.2 kg)
- Sand: 0.42 m³
- Aggregate: 0.84 m³
Optional: Water Estimate (Guidance Only)
Water depends on workability, aggregate moisture, and required strength. A common guideline is a water–cement ratio between 0.40 to 0.60.
Water (liters) ≈ Cement (kg) × w/c ratio
Example (w/c = 0.50): 403.2 × 0.50 = 201.6 liters
For site work, always consider moisture in sand/aggregate and follow engineer specs for critical structures.

Why Accurate Material Estimation Matters
- Strength & durability: incorrect cement proportion can reduce compressive strength.
- Workability: poor sand/aggregate balance affects finishing and compaction.
- Cost control: over-ordering increases waste; under-ordering delays work.
- Consistency: planned quantities help maintain uniform batches.
Practical Tips (On-Site)
- Add buffer: If you expect wastage, consider an extra 5–10% material margin.
- Check sand moisture: wet sand changes effective water and volume.
- Don’t over-water: more water can reduce strength (especially for structural work).
- For critical structures: follow a structural engineer / mix design specification.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I select the right concrete mix ratio?
- M5 (1:5:10) – For non-structural works
- M15 (1:2:4) – Residential structures
- M25 (1:1:2) – High-strength applications
- Consult a civil engineer for site-specific requirements.
2. How do I enter measurements in the calculator?
- Input total volume (m³ or ft³) directly, OR
- Enter dimensions (Length × Width × Height) in meters or feet.
3. What are the densities of common construction materials?
- Cement: 1440 kg/m³ (90 lb/ft³)
- Sand: 1600 kg/m³ (100 lb/ft³)
- Aggregate: 1450-1550 kg/m³ (90-97 lb/ft³)
4. What is the standard weight of a cement bag?
- 50 kg (110 lbs) in most regions
- 94 lb (42.6 kg) in the USA
5. Can I use a custom concrete mix ratio in the calculator?
Yes! The calculator allows users to either select a predefined mix ratio (M5 to M25) or input a custom mix ratio for unique construction requirements.
6. How do I calculate concrete for multiple areas or projects?
If you have multiple areas to cover, calculate each area separately using the dimensions input option and sum up the total volume before determining material quantities.
7. What is the standard water-cement ratio for concrete?
The water-cement ratio typically ranges between 0.4 to 0.6, depending on the required strength and workability of the concrete. A lower ratio increases strength but reduces workability.
8. Does the calculator consider wastage and extra material?
Yes, the calculator applies a 1.54 multiplier to convert wet volume into dry volume, accounting for voids in sand and aggregates. However, for on-site variations, it’s recommended to add an extra 5-10% buffer.
9. Can I use the calculator for reinforced concrete structures?
Yes, but the reinforcement (steel rebar) is not included in the calculation. This tool only estimates cement, sand, and aggregate. If reinforcement is needed, consult a structural engineer for additional material requirements.
Benefits of Using Our Concrete Calculator
✅ Precision: Avoid material shortages or excesses
✅ Time-Saving: No manual calculations needed
✅ Cost-Efficient: Reduces unnecessary material costs
✅ User-Friendly: Simple and easy-to-use interface
✅ Versatile: Suitable for home and commercial projects
Summary of Concrete Calculator Page
The Concrete Calculator is a user-friendly tool designed to provide accurate estimates of cement, sand, aggregate, and water required for different M-grade concrete mixes (M5, M7.5, M10, M15, M20, M25). By inputting either total volume or structural dimensions, users can quickly determine material quantities, ensuring cost-effective and precise construction planning.
Key Features & Benefits:
✅ Accurate Material Estimation – Avoid overuse or shortage of materials
✅ Supports Various Mix Ratios – Choose predefined or custom ratios
✅ Easy Input Options – Enter volume (m³/ft³) or dimensions (L×W×H)
✅ Prevents Wastage & Saves Costs – Optimize resource usage
✅ Applicable for Residential & Commercial Use – Versatile for all projects
How it Works:
- Select Concrete Mix Ratio (e.g., M20: 1:1.5:3)
- Enter Required Volume or Dimensions (in m³ or ft³)
- Get Cement, Sand & Aggregate Quantities
- Includes Water-Cement Ratio for Proper Mixing
For 1m³ of M20 Concrete (1:1.5:3 ratio):
- Cement – 8.06 bags (403.2 kg)
- Sand – 0.42 m³ (14.83 ft³)
- Aggregate – 0.84 m³ (29.67 ft³)
- Water – 201.6 liters
The calculator ensures structural integrity, reduces manual errors, and improves efficiency in concrete mix design, making it essential for builders, engineers, and contractors. 🚀
Refrences
1. American Concrete Institute (ACI)
- ACI PRC-211.1-22: Selecting Proportions for Normal-Density and High-Density Concrete: This guide provides procedures for selecting and adjusting concrete mixture proportions.
2. Caltrans (California Department of Transportation)
- Concrete Technology Manual: Chapter 3 offers detailed guidance on reviewing concrete mix designs.
3. Portland Cement Association (PCA)
- Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures: A comprehensive reference on concrete technology and mix design.
4. Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structures
- EN 1992-1-1: General Rules and Rules for Buildings: This standard provides technical rules for the design of concrete structures.
5. Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
- IS 10262: Guidelines for Concrete Mix Design Proportioning: This standard provides guidelines for proportioning concrete mixes.

