Concrete Calculator Software
Fast volume estimates for common concrete shapes (auto unit conversion).
Slabs, Square Footings, or Walls
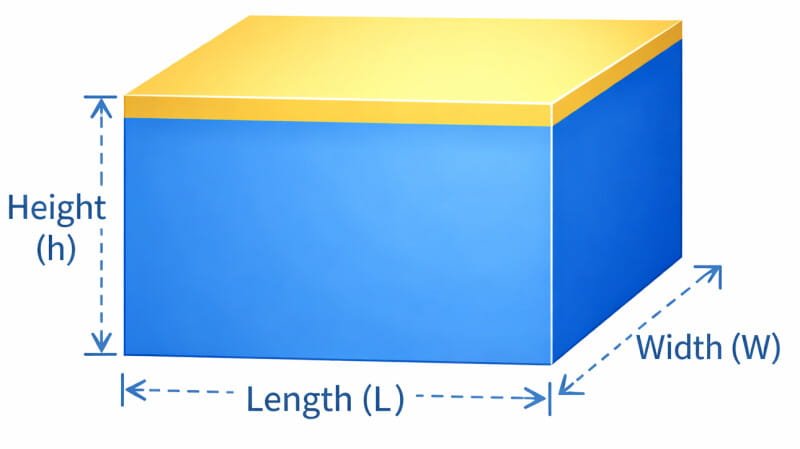
Tip: Slab thickness usually in inches (e.g., 4 in, 6 in).
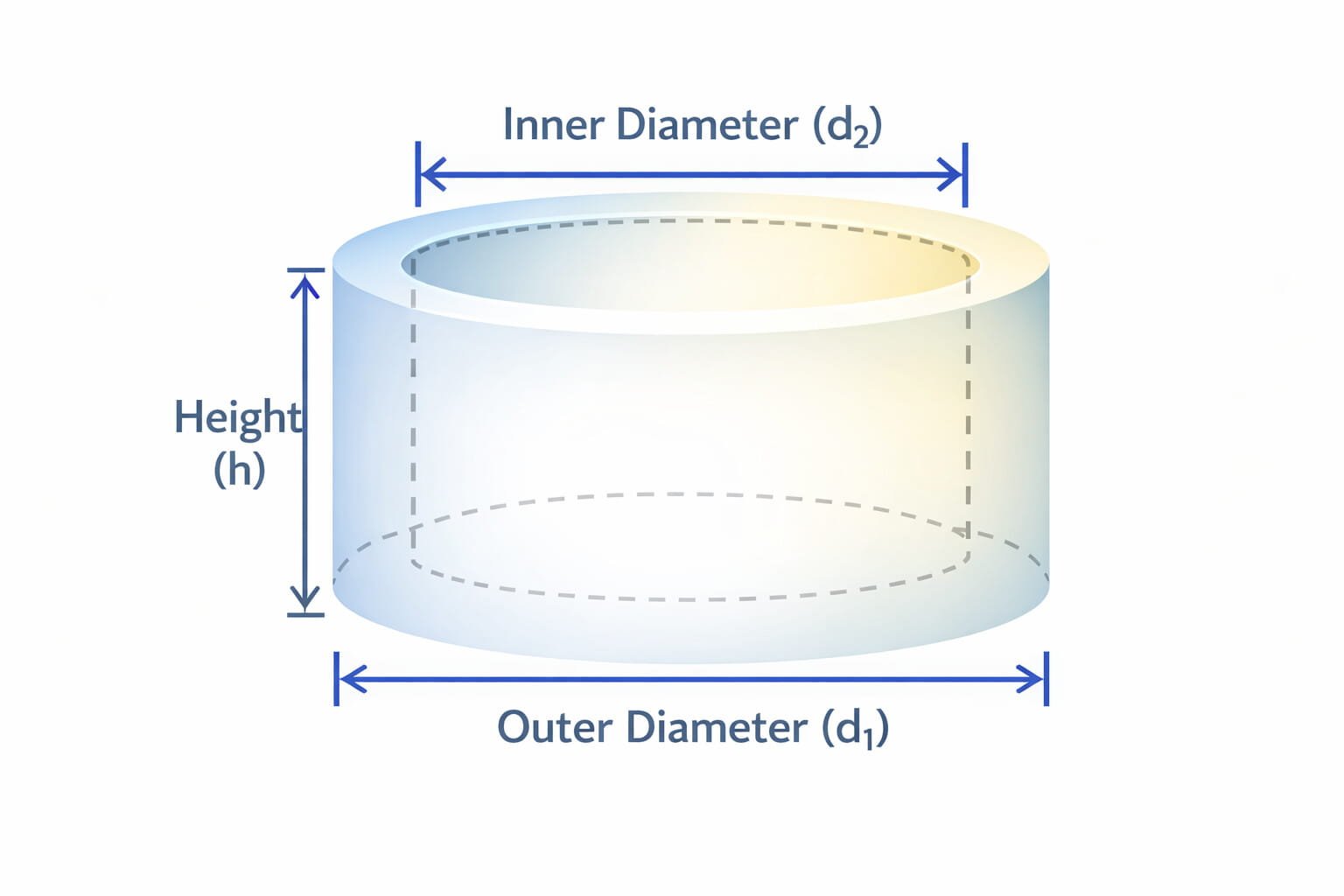
Hole, Column, or Round Footings
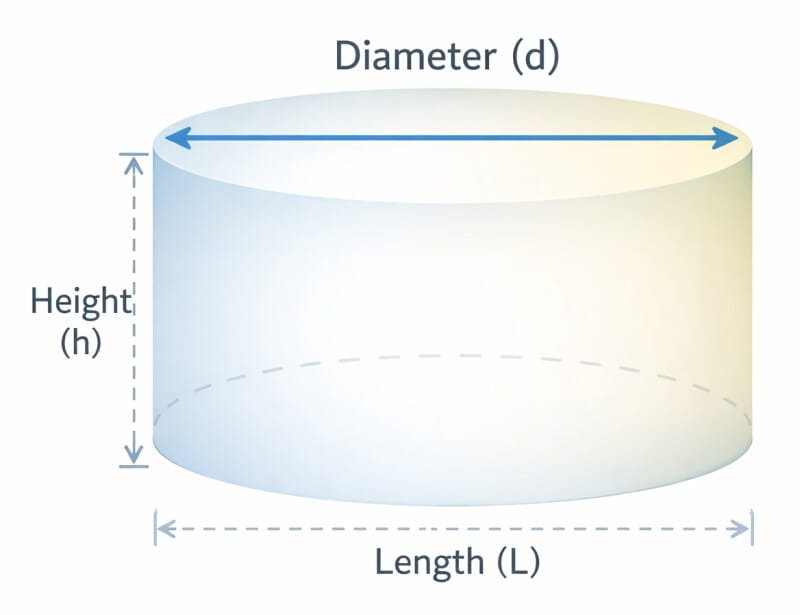
Circular Slab or Tube
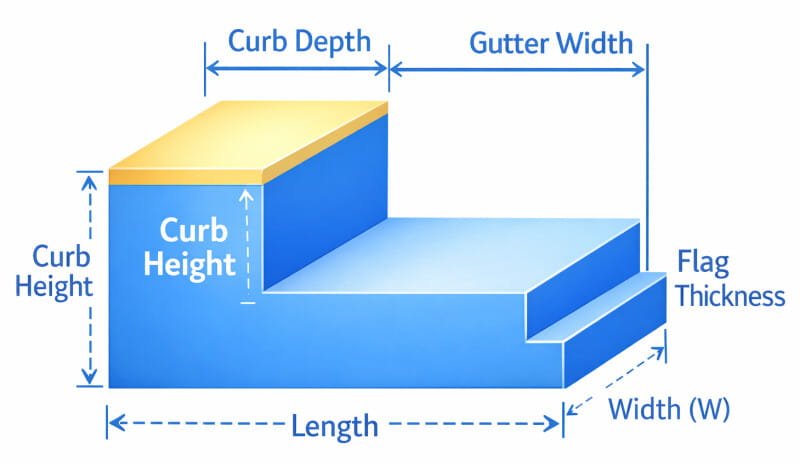
Curb and Gutter Barrier
Stairs
Improved stairs model: stepped volume uses n(n+1)/2 (more accurate than “run×rise×width×n”).
Landing is approximated as W × P × h (rise used as thickness).
Concrete Volume Unit Conversions: Cubic Feet, Yards, Meters, and Liters
| Unit Conversion | Equivalent Value |
|---|---|
| 1 cubic foot (ft³) | 0.0283168 cubic meters (m³) |
| 1 cubic meter (m³) | 35.3147 cubic feet (ft³) |
| 1 cubic yard (yd³) | 0.764555 cubic meters (m³) |
| 1 cubic meter (m³) | 1.30795 cubic yards (yd³) |
| 1 cubic foot (ft³) | 0.037037 cubic yards (yd³) |
| 1 liter (L) | 0.001 cubic meters (m³) |
| 1 cubic meter (m³) | 1,000 liters (L) |
In this page, we’ll explore the different shapes of concrete volume calculators available and provide practical examples to help you get the most accurate estimate for your project.
Slabs, Square Footings, or Walls Concrete Calculator
The Slabs, Square Footings, or Walls Concrete Calculator is ideal for projects involving rectangular or square surfaces. Whether you’re constructing a patio, floor, or wall, this calculator ensures you get precise measurements for your concrete requirements.
Formula:
- L = Length
- W = Width
- H = Height or thickness
Example Calculation:
If you’re pouring a slab that’s 20 feet long, 10 feet wide, and 4 inches (0.3333 feet) thick:
Convert this to cubic yards:
You would need approximately 2.47 cubic yards of concrete for this slab.
Hole, Column, or Round Footings Concrete Calculator
This calculator is designed to help estimate concrete volume for circular structures such as columns, round footings, or post holes. These calculations are crucial for projects that involve cylindrical shapes, such as supporting columns or deep round footings.
Formula:
- D = Diameter
- H = Height
Example Calculation:
For a column with a diameter of 4 feet and a height of 8 feet:
Convert to cubic yards:
Circular Slab or Tube Concrete Calculator
For cylindrical slabs or hollow tubes, such as piping or columns with a hollow center, this calculator provides an accurate estimate. This type of calculator is often used for construction projects involving tubes, pipes, or hollow columns.
Formula:
- D1 = Outer diameter
- D2 = Inner diameter
- H = Height
Example Calculation:
For a hollow tube with an outer diameter of 5 feet, an inner diameter of 3 feet, and a height of 10 feet:
Convert to cubic yards:
Curb and Gutter Barrier Concrete Calculator
This calculator is especially useful for estimating the concrete required for curbs and gutter barriers, typically used in road or sidewalk construction. The calculations include both the curb and gutter volume, giving an accurate estimate for both sections.
Formula:
- Curb Volume (fixed):
- Gutter Volume:
- Total Volume:
Example Calculation:
For a curb that is 6 inches deep, 12 inches tall, flag thickness 6 inches, with a gutter width of 10 inches, and a length of 40 feet:
Total volume:
Convert to cubic yards:
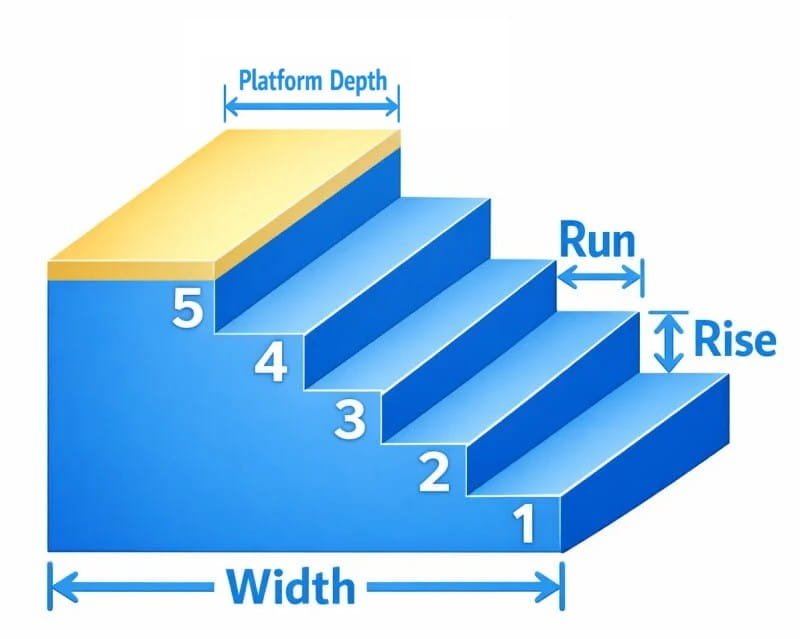
Stairs Concrete Calculator
The Stairs Concrete Calculator is used to estimate the concrete required for constructing stairs, including platforms if applicable. It takes into account the run, rise, and width of each step, as well as the number of steps.
Formula (fixed):
Example Calculation:
For a set of stairs with a run of 12 inches (1 ft), a rise of 7 inches (0.5833 ft), a width of 4 feet, and 5 steps:
Adding the platform with a depth of 3 feet:
Total volume:
Convert to cubic yards:
Concrete Calculator FAQs
Choose a category on the left to view related frequently asked questions. (Formulas render as real math automatically.)
General Concrete Volume FAQs
How do I calculate concrete volume for a slab?
To calculate slab volume, multiply length, width, and thickness (in feet) to get cubic feet: \[ V = L \times W \times H \] Convert cubic feet to cubic yards by dividing by 27: \[ \text{Cubic Yards}=\frac{\text{Cubic Feet}}{27} \] Example: a \(10\times10\) slab at \(4\) inches thick needs about \(1.23\) cubic yards.
What’s the formula to calculate concrete for footings or walls?
Use: \[ V = L \times W \times H \] (all in feet), then: \[ \text{yd}^3=\frac{\text{ft}^3}{27} \] For irregular shapes, split into smaller rectangles, calculate each, and sum.
How much concrete do I need for a 10×10 slab?
For a \(10\times10\) slab at 4 inches thick: \[ V = 10 \times 10 \times \frac{4}{12} = 33.33\ \text{ft}^3 \] Convert to cubic yards: \[ V=\frac{33.33}{27}=1.23\ \text{yd}^3 \] Add \(5\%-10\%\) extra for waste/spillage.
How to convert cubic feet to cubic yards for concrete?
Divide cubic feet by 27: \[ \text{yd}^3=\frac{\text{ft}^3}{27} \] Example: \[ \frac{100}{27}=3.70\ \text{yd}^3 \]
How much does a cubic yard of concrete cover?
A practical rule: \(1\ \text{yd}^3\) covers about \(81\ \text{ft}^2\) at 4 inches thick, and about \(54\ \text{ft}^2\) at 6 inches thick (coverage changes with thickness).
Do I need to account for waste when ordering concrete?
Yes—add \(5\%-10\%\) extra. If your estimate is \(2.0\ \text{yd}^3\), order about \(2.1\) to \(2.2\ \text{yd}^3\).
Slabs, Square Footings, or Walls
How thick should a concrete slab be?
Patios/walkways commonly use \(4\) inches. Driveways/garages often use \(6\) inches for heavier loads. Always check local codes and soil conditions.
How to calculate concrete for a 4-inch slab?
Convert thickness: \(4\ \text{in}=\frac{4}{12}=0.33\ \text{ft}\). Example \(20\times20\): \[ V = 20 \times 20 \times 0.33 = 132\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{132}{27}=4.89\ \text{yd}^3 \]
What’s the concrete volume for a 20×20 slab?
At 4 inches thick: \[ V = 20 \times 20 \times \frac{4}{12} = 133.33\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{133.33}{27}=4.94\ \text{yd}^3 \] Add \(5\%-10\%\) waste.
How to adjust calculations for irregularly shaped slabs?
Split the shape into rectangles/squares, compute each with \(V=L\times W\times H\), then add them. Curves can be approximated using segments.
How much concrete do I need for a footer or foundation wall?
Example: \[ V = 30 \times 1 \times 2 = 60\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{60}{27}=2.22\ \text{yd}^3 \]
Holes, Columns, or Round Footings
How to calculate concrete for a round column or sonotube?
Use cylinder volume: \[ V=\pi r^2 h \] Example: 12-inch diameter \(\Rightarrow r=6\ \text{in}=0.5\ \text{ft}\), \(h=4\ \text{ft}\): \[ V=3.14\times(0.5)^2\times 4=3.14\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{3.14}{27}=0.12\ \text{yd}^3 \]
How much concrete for a 12-inch diameter hole?
Same as above (per hole): \[ V=3.14\times(0.5)^2\times 4=3.14\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{3.14}{27}=0.12\ \text{yd}^3 \]
What’s the concrete volume for a fence post hole?
Typical 6-inch diameter \(\Rightarrow r=3\ \text{in}=0.25\ \text{ft}\), depth \(=2\ \text{ft}\): \[ V=3.14\times(0.25)^2\times 2=0.39\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{0.39}{27}=0.014\ \text{yd}^3 \]
How to estimate concrete for pier footings?
For each pier: \[ V=\pi r^2 h \] Add all pier volumes and convert: \[ \text{yd}^3=\frac{\text{ft}^3}{27} \]
Circular Slabs or Tubes
How to calculate concrete for a circular slab?
Use: \[ V=\pi r^2 t \] Example: 10-ft diameter \(\Rightarrow r=5\), thickness \(6\ \text{in}=0.5\ \text{ft}\): \[ V=3.14\times 5^2\times 0.5=39.25\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{39.25}{27}=1.45\ \text{yd}^3 \]
How much concrete for a 20-foot diameter circular patio?
20-ft diameter \(\Rightarrow r=10\), thickness \(4\ \text{in}=\frac{4}{12}\ \text{ft}\): \[ V=3.14\times 10^2\times \frac{4}{12}=104.67\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{104.67}{27}=3.88\ \text{yd}^3 \]
What’s the difference between a circular slab and tube volume?
A slab is solid; a tube is hollow: \[ V=\pi\left(R^2-r^2\right)h \] (outer minus inner).
Curb and Gutter
How to calculate concrete for curb and gutter?
One common estimating approach is curb + gutter components: \[ V_{\text{curb}}=\text{Depth}\times(\text{Height}+\text{Flag Thickness})\times \text{Length} \] \[ V_{\text{gutter}}=\text{Gutter Width}\times \text{Flag Thickness}\times \text{Length} \] Total: \[ V_{\text{total}}=V_{\text{curb}}+V_{\text{gutter}} \] Then convert \(\text{yd}^3=\frac{\text{ft}^3}{27}\).
What’s the standard cross-section size for residential curbs?
Curb profiles vary by region/standard drawings. A commonly used estimate example is around 6 inches wide and 18 inches tall, but always verify local details.
How much concrete for 100 feet of curb and gutter?
If cross-section area \(A=0.75\ \text{ft}^2\) and length \(L=100\ \text{ft}\): \[ V=A\times L=0.75\times 100=75\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{75}{27}=2.78\ \text{yd}^3 \] Add \(5\%-10\%\) waste.
Barriers (Retaining Walls, etc.)
How to estimate concrete for a retaining wall?
\[ V=L\times H\times T \] Example: \[ V=20\times 3\times 1=60\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{60}{27}=2.22\ \text{yd}^3 \]
Do I need to include rebar volume in calculations?
Rebar volume is usually negligible for estimating concrete. Focus on dimensions and add \(5\%-10\%\) extra for waste.
How much concrete for a 10-foot-long barrier wall?
\[ V=10\times 2\times 1=20\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{20}{27}=0.74\ \text{yd}^3 \]
Stairs
How to calculate concrete for stairs?
A quick and more accurate stepped model: \[ V_{\text{steps}} = W \times G \times h \times \frac{n(n+1)}{2} \] Landing approximation: \[ V_{\text{landing}} \approx W \times P \times h \] Total: \[ V_{\text{total}} = V_{\text{steps}} + V_{\text{landing}} \]
How much concrete for 5 steps with a landing?
Estimate steps + landing separately, then convert cubic feet to cubic yards by dividing by 27: \[ \text{yd}^3=\frac{\text{ft}^3}{27} \] Add \(5\%-10\%\) waste for outdoor pours.
What’s the average concrete volume for outdoor stairs?
Often \(0.5\)–\(1.0\ \text{yd}^3\) depending on size. Measure run, rise, width, and steps for accurate results.
Tools and Advanced Questions
Are online concrete calculators accurate?
They’re accurate if inputs are correct. For complex geometry or structural work, verify manually or consult a professional.
How to use a concrete volume calculator for multiple shapes?
Break the project into shapes, calculate each volume, then sum the results. Many calculators support combining volumes.
What’s the best free concrete calculator app?
Look for an app/web tool that supports slabs, footings, round holes, and unit conversions. Web calculators are often enough for most users.
How to calculate concrete cost per cubic yard?
\[ \text{Cost} = (\text{Total yd}^3)\times(\text{Price per yd}^3) + \text{Delivery/fees} \] Prices vary by region.
How to adjust for slopes or uneven terrain in concrete volume?
Take multiple depth readings and use the average thickness in your volume calculation.
Material-Specific FAQs
Does gravel or base material affect concrete volume?
Base material is separate from concrete volume. It supports the slab but doesn’t change concrete volume unless slab thickness changes.
How to calculate concrete bags (60lb, 80lb) needed?
Typical yields: \(60\text{lb}\approx 0.45\ \text{ft}^3\), \(80\text{lb}\approx 0.60\ \text{ft}^3\). Bags needed: \[ \text{Bags}=\frac{\text{Total ft}^3}{\text{Yield per bag}} \] Example: \(100\ \text{ft}^3 \div 0.45 \approx 222\) bags (60lb).
How much concrete for a 400 sq ft garage floor?
At 6 inches (\(0.5\ \text{ft}\)) thick: \[ V=400\times 0.5=200\ \text{ft}^3 \] \[ V=\frac{200}{27}=7.41\ \text{yd}^3 \] Add \(5\%-10\%\) waste.





Comments are closed.